Usage of the Composum AI for AEM
Large language models like ChatGPT increasingly provide often near human level capabilities in using languages, and exhibit serious reasoning capabilities and offer an incredible breadth of general knowledge. The Composum AI provides the editor in Adobe AEM with a seamless integration that allows analysing content, content generation and transformation according to the users wishes. The Composum AI for AEM provides the editor in Adobe AEM with a seamless AI integration that allows analysing text content, content generation and transformation according to the users wishes. It provides two assistant dialogs It integrates two assistant dialogs with different focus and capabilities, which are documented in the following sections:
- the Content Creation Assistant can be called from component dialogs and richtext editors and is focused on creating textual content that can be integrated into your pages,
- the Side Panel AI can be called from the page editor and the experience fragment editor and is focused on analysing, discussing and improving the content of your pages.
A quick demo
The content creation assistant
How to access the content creation assistant
There are two ways to access content creation dialog. If the Composum AI is enabled, you will find a new icon (gears and pen) in the toolbar of richtext editors. It will call up the Content Creation Dialog. The content created with it can then either replace the richtext editor's content and be edited further or the edit be aborted, if needed, or the dialog can be cancelled, returning to an unmodified richtext editor.
The dialogs are currently accessible in the AEM page editor, the page properties and the experience fragment editor.
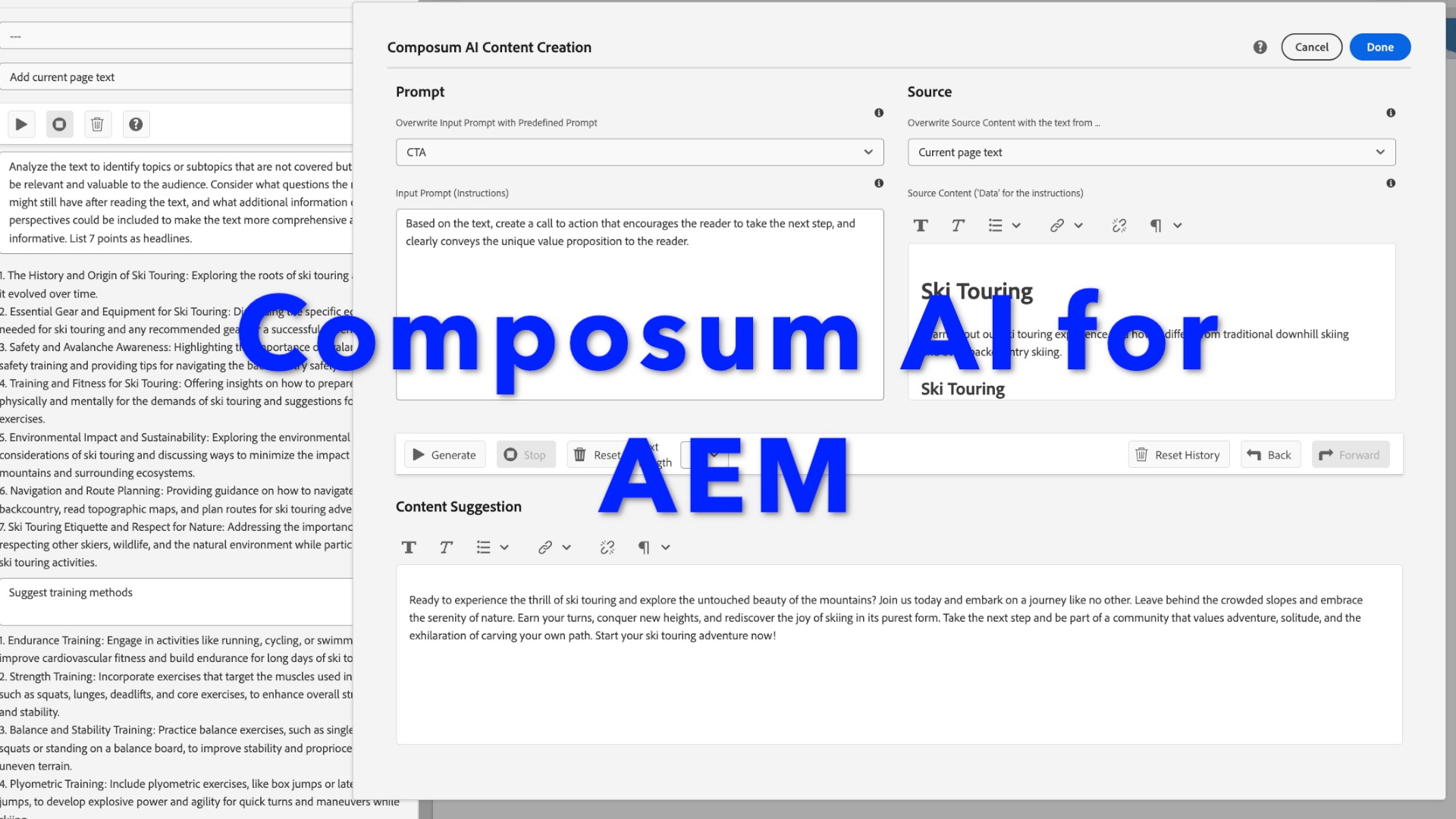
Functionality of the content creation assistant
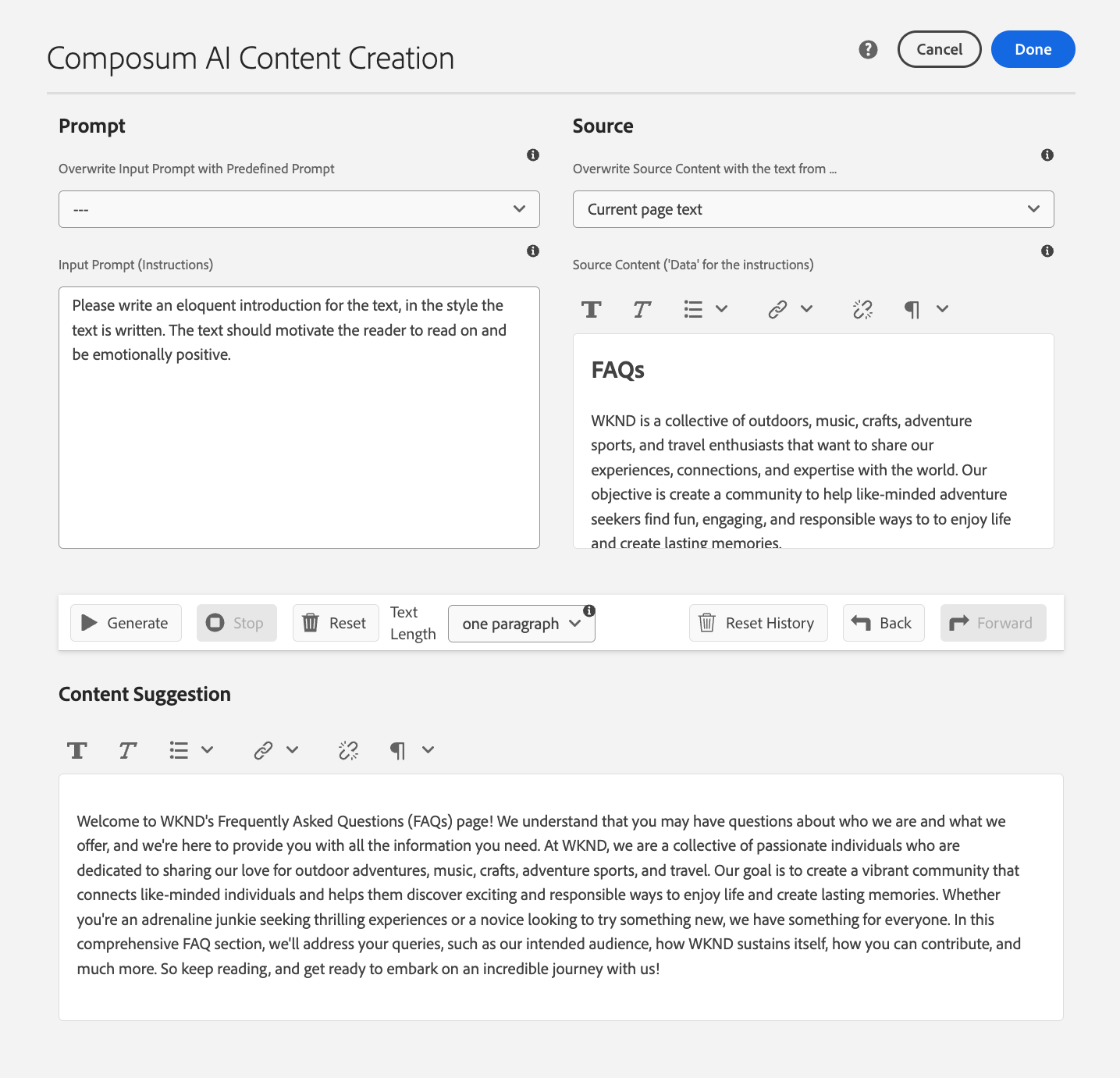
This dialog provides access to a powerful and flexible tool the Composum AI offers for creating content.
First, it allows you to select a base text for the AI to draw from. That can be the text field you were editing when calling up the dialog, it can be the text content of the component you were editing or the text content of the current page. But you can also take the last output of the AI, to have it refine the text iteratively, paste in an external text or just describe what you need without providing any additional base text.
Then you can either select one from a range of predefined prompts, like Summarize, Introduction, Conclusion, Expand, Headline suggestions, Improve, …, and apply these. You are invited to modify or extend the prompt you selected, or create your entirely own request to the AI.
A history in the dialog supports you to switch back and forth between your requests, so it's easy to retry and switch back if the first generated text was better.
There is also a “Last prompts” drop down menu that sets the prompt and content selector (if applicable) to the last values that have been used to generate content. In contrast to the history this feature retains its data across sessions in the current browser and is independent of the currently edited component, making it a useful tool for applying similar prompts to different components or pages.
As the last step, you can replace the edited component field by the generated text, or cancel the operation. The calling dialog / the richtext editor from which the content creation was called will still be open for editing.
Text sources (base text)
Selecting one of these options replaces the ‘Source’ text area with the chosen text.
- Text field: The AI is provided with the text contained in the field you were editing.
- Component: The text content of the component you were editing, including subcomponents. Useful e.g. for suggesting headlines for components or sections.
- Current Page: The text content of the current page. Useful e.g. for writing summaries, introductions, page descriptions etc.
- Last Output: The current content suggestion shown in this dialog, for iterative improvement of a text.
- Hand edited content: You can provide your own text as a base for the AI to work with.
- No Text Added: If you like to generate text by just giving the AI some instructions that do not refer to any current text content, this is your choice.
- External URL: An URL field is provided, where you can enter the URL of a web page. The text content of the URL will be retrieved into the ‘Source’ text area.
- If the component itself or sibling components contain paths into the JCR - e.g. links to other pages or references to parts of other pages - then up to 5 of these paths are listed as additional options. Selecting one of these options replaces the ‘Source’ text area with the chosen text.
- If some of those references are images, these will be offered as well. The images can serve as input for the AI ( currently the beta version of ChatGPT vision preview) e.g. to generate a description for the image.
Predefined prompts
The predefined prompts are valuable as they are, but please take them as an inspiration what you can do with the text. Please note that it is possible to replace the predefined prompts with your own library of prompts. Some examples are:
- Summarize: The selected text is summarized.
- Introduction: The AI writes an introduction for the text.
- Conclusion: The AI writes a conclusion for the text.
- Expand: The AI uses the provided notes as inspiration to write a text that expresses the main ideas and themes present in a businesslike informative style.
- Headline: The AI writes a headline for the text in a businesslike informative style.
- 10 headline suggestions: The AI provides10 headline suggestions for the text in a businesslike informative style.
- 10 headline + subheadline suggestions: The AI provides10 headline and subheading suggestions for the text in a businesslike informative style.
- Question: The AI answers a question based on the given text.
- Improve: The AI improves the text into a businesslike informative style, fixing orthographical and grammar errors.
- SEO Description: The AI creates a description for a web page with the given text, usable for search engine optimization (SEO).
- Describe Image: somewhat experimental: the AI describes a selected image.
Tips and Tricks for using the Content Creation Assistant
To use the make an excerpt from or rewrite of an existing text, you can copy and paste that text into the existing dialog field and select the text field as base text, or paste it into the content suggestion field and select that as base text, and then specify in the prompt what you want to be done.
The dialog can be maximized to accomodate more text, and there is also a help window accessible with the “?” icon.
If you are not satisfied with the generated text, there are several ways to improve it:
- You can simply retry by pressing the “Generate” button again.
- You can add hints to the prompt how the text should be written. For example “Use passive voice and an informative style.” or “Make the text engaging and motivating.”
If you want to generate headlines for a component, you could select the component's text as base text and use the “10 suggestions for headline” prompt. Generally, to get ideas for short texts it can be a good idea to ask the AI to list a number of suggestions.
Even though that's not the primary use of the assistant, you can (creatively) use it to get answers from the AI about general questions, or have it use the page content to answer your questions. Just open the assistant on any text field in the page, use “current page text” as base text or even “no text” and ask away. Of course you might want to press " Cancel" after such use.
The Side Panel AI
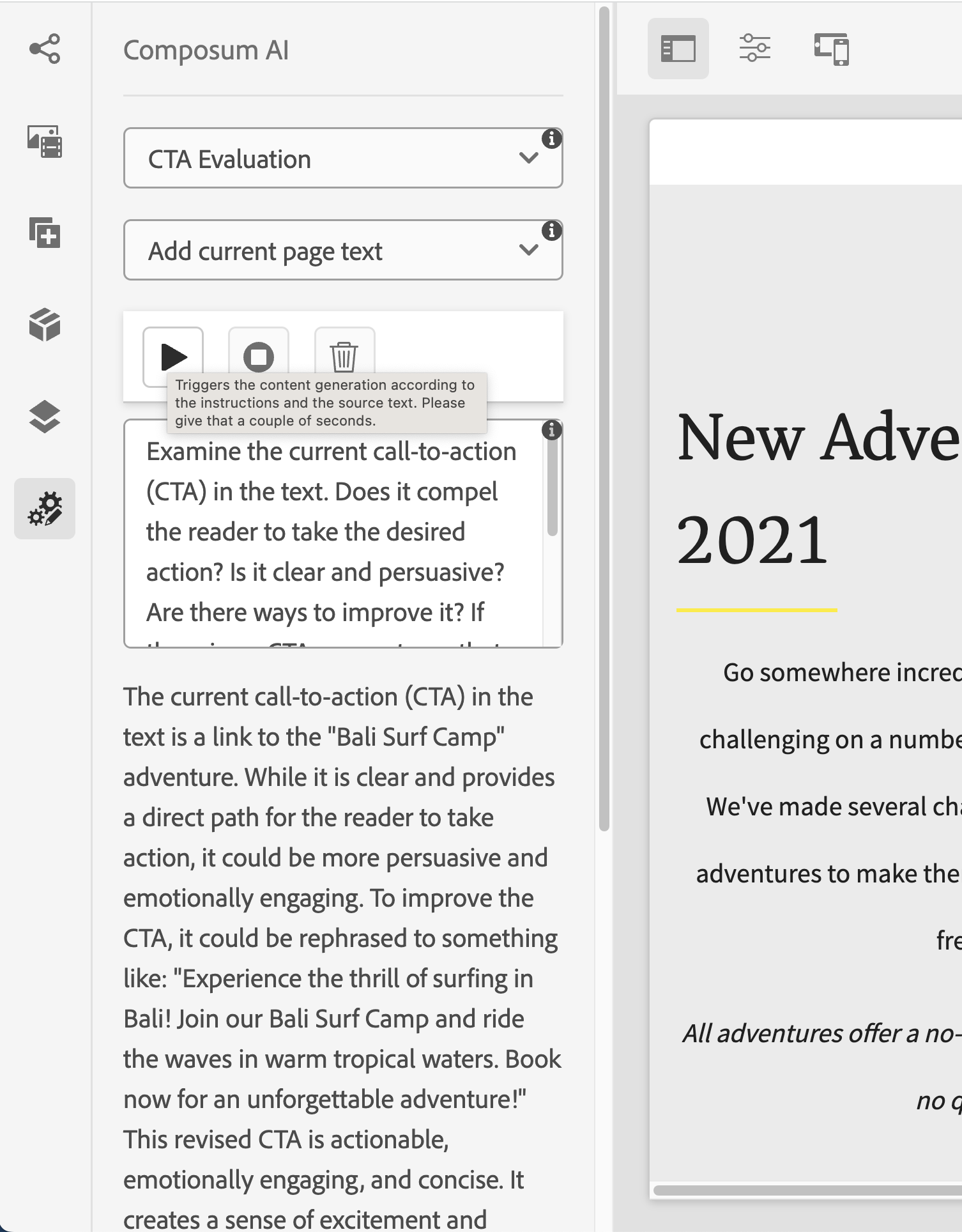
The Sidebar AI is a complement to the content creation assistant whose primary focus is not on content generation, but employing the AI's reasoning capabilities to generate reports about the text content of the page or individual components. Its purpose is to assist you in improving the content or seek explanations through a chat with the AI.
Similar to the Content Creation Assistant, the Sidebar AI enables you to select a base text for the AI to work with, such as the current page's text, or the text content of a selected component along with its subcomponents. Then you can either select one of a range of predefined prompts, or write your own request to the AI. The predefined prompts range from text / content flow review, suggestions for simplification, to suggestions for “call to action” phrases, and, of course, you can provide your own. If you are not yet satisfied with the result, you can both modify the prompt and try again, or ask for further refinement or additional information in a chat like fashion.
Text sources (base text)
- Page: The text content of the current page.
- Component: The text content of the selected component including subcomponents.
- No additional source: If you like to discuss / chat without referring to any current text content, this is your choice.
Predefined prompts
We collected a number of prompts that might be useful for you when improving the text. As always, please feel free to extend / clarify / refine them, or to write your own requests. (Again, please note that it is possible to replace the predefined prompts with your own library of prompts.) Among the default prompts are:
- Review: The text is checked for good text flow, contradictions, repetitions, redundancy, etc.
- Content Flow: Checks for problems with the flow of the tex
- Question: The AI answers a question based on the provided text.
- 10 headline suggestions: Ten headline suggestions for the text are generated using a businesslike informative style.
- Summary: A brief summary of the main points and themes in the text is generated.
- Simplification Suggestions: Identifies parts of the text that could be simplified and provides alternative suggestions..
- CTA Suggestions: Five distinct call-to-action (CTA) phrases are suggested to motivate further engagement with the content or brand.
- Content Gap Analysis: Tries to identify relevant topics or subtopics that are not covered.
- Relevance Evaluation: The content of the text is evaluated to determine if it is relevant to a specific topic or purpose.
Using the Chat feature
In this dialog there are several ways to improve the result. It is possible to edit the prompt and resend it (or even just retry), and it is possible to use a chat to ask further questions about the response and have the AI elaborate. At the bottom of reach response appears a new prompt input field, where it's possible to continue in a conversation. There is, however, a limit in the length of conversations, so it's better to start fresh when the topic is changed. You can always go back using the history, and even continue the old conversation, which will be saved as a new history entry.
Conclusion
The Composum AI module brings you many new abilities for AI text generation and analysis to the AEM author, supported by large language models like ChatGPT in a seamless integration into Composum Pages. Please give it a try, tell us what you think, and enjoy using it creatively for your site!